Plant Dashboard
Plants
Ever since my move to a new apartment, I have been more interested in plants. Ott’s Exotic Plants in Phoenixville is a great place to find cool plants! I bought a few for my new place and wanted a fun way to track their watering or whether I could create an automatic watering process (so this project is somewhat of a first step).
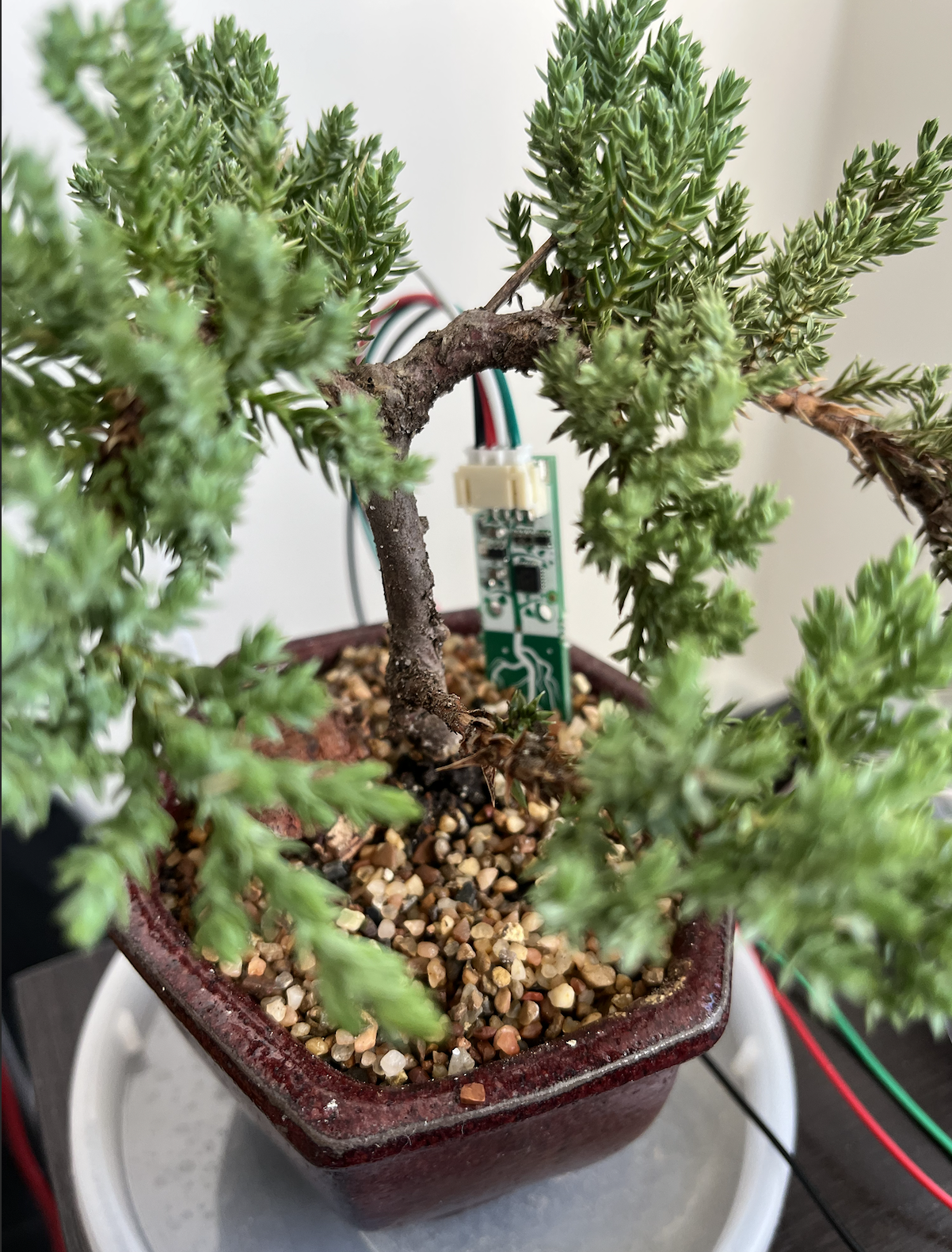
Moisture and Temperature Sensor
I used the Adafruit Moisture Sensor in conjunction with my Raspberry Pi to monitor my plant’s temperature level and moisture level.

Python Code
I wrote some simple python code that reads the moisture and temperature of each sensor and sends the data to my Supabase database.
The “read” function:
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 ladyada for Adafruit Industries
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
import time
from datetime import datetime
import board
from adafruit_seesaw.seesaw import Seesaw
from Send_Data import supa_send
import adafruit_bitbangio as bitbangio
import digitalio
# uses board.SCL and board.SDA
i2c_bus = board.I2C()
# Define pins for the second I2C bus
i2c2_sda = board.D27 #13 #board.D33 #13
i2c2_scl = board.D22 # 15 # board.D10 # 15
# Create the second I2C bus
i2c2 = bitbangio.I2C(i2c2_scl, i2c2_sda)
# Initialize the first moisture sensor
ss = Seesaw(i2c_bus, addr=0x36)
# Initialize the second moisture sensor
ss2 = Seesaw(i2c2, addr=0x36)
# Table list (for now just the one)
table = "time_temp_humidity_1"
# data list create
datalist = []
# read moisture level through capacitive touch pad
touch = ss.moisture_read()
# Read moisture from second sensor
touch2 = ss2.moisture_read()
# read temperature from the temperature sensor
temp = ss.get_temp()
temp2 = ss2.get_temp()
# Convert to degrees fahrenheit
temp_F = temp*(9/5) + 32
temp2_F = temp2*(9/5) + 32
# Time
now = datetime.now()
t = now.strftime("%I:%M:%S %p, %m/%d/%Y")
# package data as a JSON
data = {'time': t, 'moist': touch, 'temp': temp_F, 'temp2': temp2_F, 'moist2': touch2}
# append the data to the list
datalist.append(data)
print(datalist)
# Send data to the Supabase database
supa_send(data, table)
The “send” function:
import requests
from supabase_py import create_client
# Supabase project details
sb_url = 'YOUR-URL-HERE'
sb_key = 'YOUR-KEY-HERE'
# supbabase package stuff
sb = create_client(sb_url, sb_key)
# Function to send data to Supabase
def supa_send(data, table):
# send the data using supabase package
insert_data = sb.table(table).insert(data).execute()
print(insert_data)
print("Data sent to Supabase.")
Supabase
I save a reading from the sensors every 5 minutes to my Supabase database using a CRON job. This simple SQL table houses the time the reading was taken as well as the moisture and temperature reading from each sensor.
Flask Application
By running a flask application on my local internet I can query a set range of data from the Supabase database and display it in a dashboard format using HTML code (see the Plant Dashboard repository for more on the code).
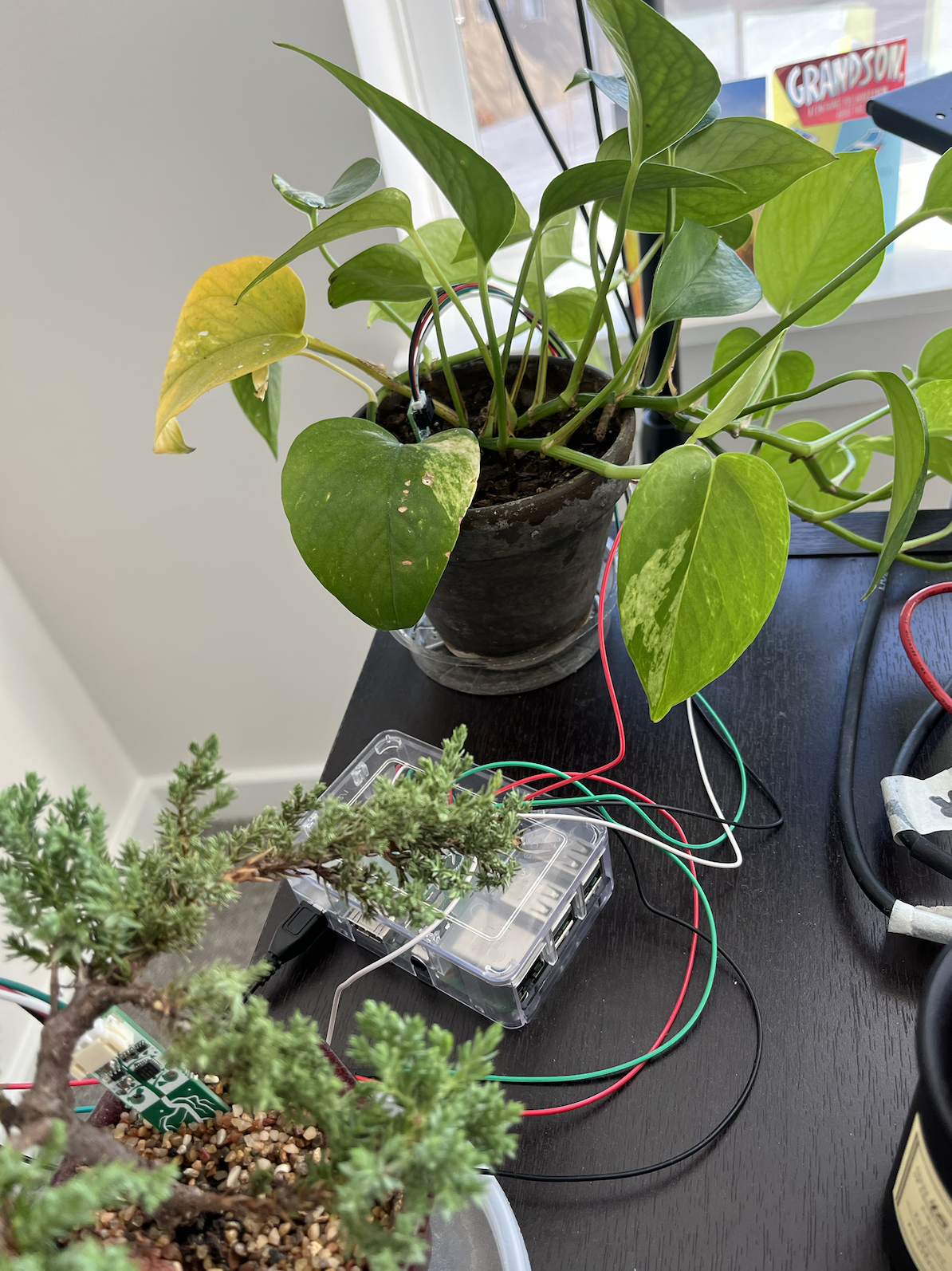
I was able to clone the i2c bus on the Raspberry pi to a separate GPIO pin so that I can run two sensors at once! My Juniper Bonsai tree and Pathos plats are both happy!

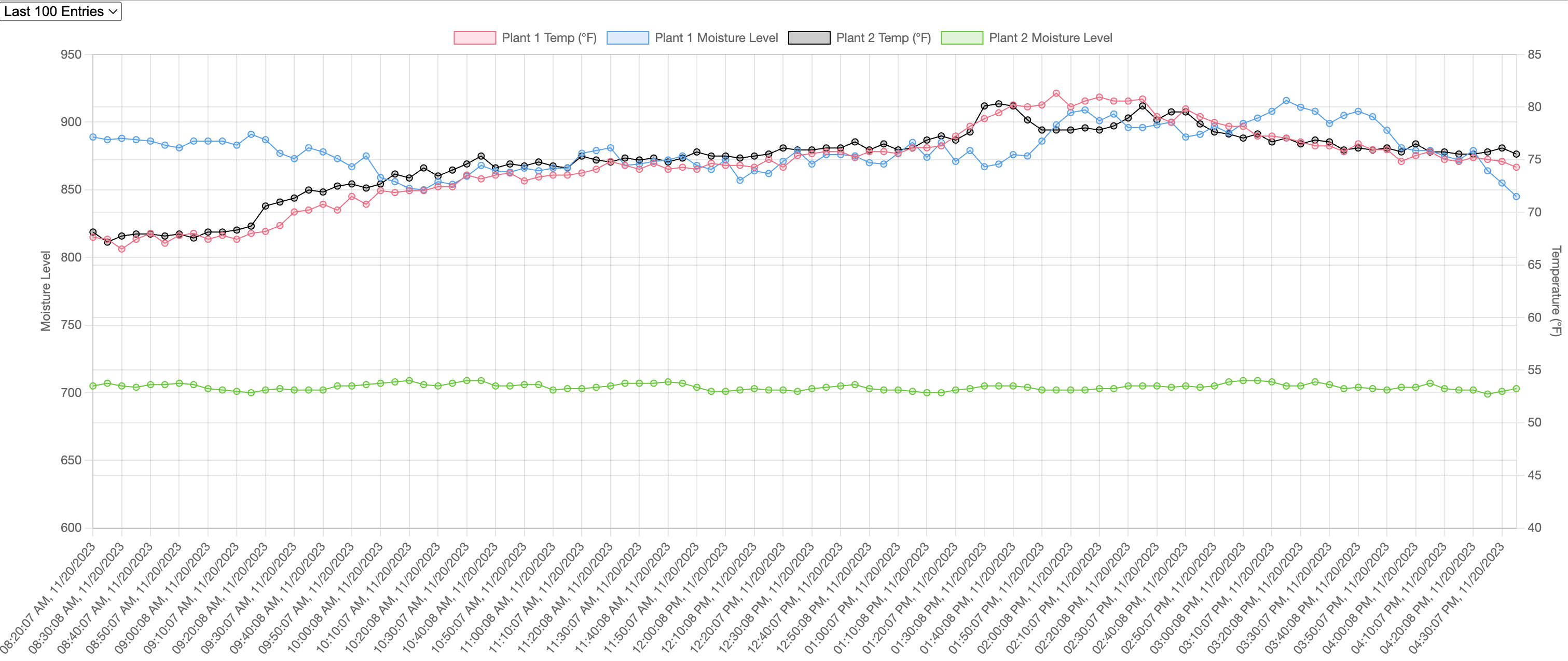
Dashboard
See the Plant Dashboard Github Repository for the full code!